What is sustainable clothing manufacturing?
Sustainable clothing manufacturing, in simple terms, is the production of clothing that respects both humans and the earth. It’s an all-encompassing term that refers to clothing produced with eco-friendly resources, ethical labour practices, and a minimized carbon footprint.
For instance:
Brand ‘X’ might source organic cotton, which requires less water and no harmful pesticides to grow, thereby safeguarding the environment.
On the other hand, Brand ‘Y’ might ensure their garment workers receive fair wages and safe working conditions, thus respecting human rights. Both brands are embracing sustainability, although their methods differ.
- Eco-friendly resources: This involves the use of organic or recycled materials, non-toxic dyes, and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
- Ethical labour practices: Ensuring that workers are paid a living wage, work in safe conditions, and are not exploited.
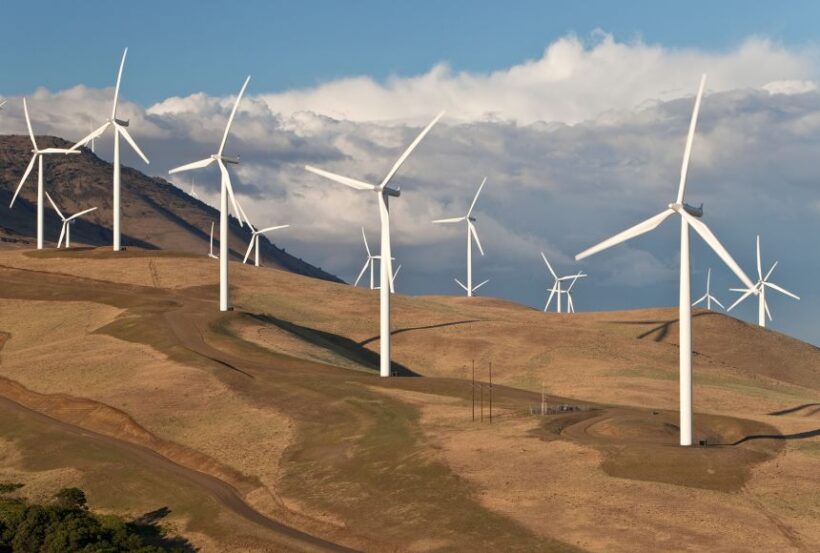
- Minimized carbon footprint: This could mean producing clothes locally to reduce shipping emissions or using renewable energy sources in factories.
Therefore, sustainable clothing manufacturing isn’t a single, fixed approach, but a broad umbrella of strategies all aimed at reducing harm and creating a positive impact on the world.
What are the benefits of sustainable clothing manufacturing?
Sustainable clothing manufacturing has a multifaceted appeal, delivering benefits on a social, environmental, and business level. From preserving our planet to boosting a brand’s image, the advantages are plentiful and impactful.
Social and Environmental Benefits
First and foremost, sustainable clothing manufacturing fosters a healthier environment. By prioritising eco-friendly materials and processes, the industry can significantly reduce its carbon footprint. This practice not only conserves natural resources but also minimises waste and pollution.
- Conservation of Resources: By using organic, recycled, or renewable materials, sustainable fashion reduces the strain on our planet’s resources.
- Waste Reduction: Sustainable practices, such as zero-waste design and recycling initiatives, can dramatically decrease waste production.
- Decreased Pollution: With less reliance on harmful chemicals and synthetic materials, sustainable clothing manufacturing can mitigate the fashion industry’s contribution to environmental pollution.
Furthermore, sustainable clothing manufacturing can encourage fair labour practices, promote social equity, and improve worker’s wellbeing. It’s a giant leap towards a more equitable fashion industry.

Business Incentives
From a commercial perspective, the benefits of sustainable manufacturing are plentiful. The practice of sustainability often bolsters a brand’s standing, fuels patron loyalty, and amplifies market presence. Today’s consumer is highly cognisant and places a premium on ethical conduct, thereby elevating sustainability as a pivotal business advantage.
“Opting for sustainability is not solely a moral decision but also a shrewd business manoeuvre.”
Exploring the Business Incentives of Sustainable Manufacturing
- Enhanced Reputation: A commitment to sustainable practices often fortifies a brand’s image, distinguishing it as a socially responsible entity.
- Inflated Customer Loyalty: Sustainable brands tend to command an enhanced degree of customer loyalty as the modern consumer values eco-friendly and ethical practices.
- Expanded Market Share: The appeal of sustainability can often translate into a larger share of the market, as consumers increasingly lean towards brands that prioritise the environment.
Moreover, adopting sustainable methodologies can result in more streamlined operations, cutting expenses over time. Incentives provided by governments to promote sustainable practices can add an extra layer of appeal. In essence, sustainable clothing manufacturing synchronises business processes with long-term aspirations and targets, laying a sturdy foundation for sustained success within the fashion realm.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Nearshoring for Sustainability vs Offshoring in the Far East?
For brands and retailers, the choices made in sourcing directly impact the sustainability of their operations. Where you source from can influence your carbon footprint, ethical trade practices, and even the quality of your products. As you venture into this crucial stage, it’s important to carefully consider your options. Next we will discuss the difference between nearshoring and offshoring, examining the pros and cons of each and helping you find the best fit for your sustainable fashion brand.
Deciding between nearshoring and offshoring in the Far East is a significant decision for sustainable fashion brands. Each option has distinct advantages and disadvantages that fashion retailers need to weigh before making the final call.
Pros of Nearshoring:
- Lower Transportation Costs: Nearshoring reduces the distance between the manufacturer and the retailer, significantly lowering transportation costs and the associated carbon footprint.
- Improved Communication: The geographical proximity allows for easier communication and alignment on sustainability standards and quality control. This can result in fewer misunderstandings and reworks.
- Fast Delivery: Shorter shipping distances make for faster delivery times, allowing businesses to respond quickly to trend changes and customer demands.
Cons of Nearshoring:
- Higher Manufacturing Costs: Labour and production costs in nearshore countries are typically higher compared to the Far East.
- Less Skilled Labour: The skill level of workers in some nearshore locations may not match that of their Far East counterparts, potentially affecting product quality.
- Limited Capacity: Nearshore manufacturers might not have the same production capacity as those in the Far East, potentially affecting large-scale production.
Pros of Offshoring in the Far East:
- Lower Production Costs: Offshoring in the Far East can lead to significant savings on labour and production costs.
- Large Scale Production: Far East manufacturers often have the capacity for large-scale production, making them a good fit for brands looking to produce at a larger scale.
- Highly Skilled Labour: Many Far East countries have a rich history in textile manufacturing and can offer highly skilled labour.
Cons of Offshoring in the Far East:
- Longer Lead Times: The geographical distance can result in longer shipping times, and thus longer lead times for product delivery.
- Communication Difficulties: Time zone differences and language barriers can lead to communication challenges, potentially affecting quality control and compliance with sustainability standards.
- Higher Carbon Footprint: The longer shipping distances involved in offshoring can result in a higher carbon footprint, which could contradict a brand’s sustainability ethos.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Approach for Your Company
Choosing the most suitable manufacturing method for your brand can be a bit of a conundrum. Whether you’re a start-up, an e-commerce company, a mid-sized retailer or a large international retail brand, your needs and capabilities vary greatly. So, here’s a bit of a guide to help you navigate these waters.
Start-up Brands
As a start-up, you’re probably looking for ways to keep costs low while also building a robust and ethical supply chain. Nearshoring could be your best bet. The shorter lead times and easier communication could benefit your lean team and tight timelines. Plus, the smaller carbon footprint aligns with a sustainable ethos.
E-commerce Companies
When running an e-commerce brand, speed is everything. Nearshoring offers faster shipping times, which can significantly enhance customer satisfaction. This approach also reduces potential communication difficulties, ensuring quality control and sustainability standards are upheld.
Mid-sized Retailers
As a mid-sized retailer, you might have the capacity for a bit of both – nearshoring for speed and customer satisfaction, and offshoring for cost advantages. It’s a balancing act, but the diversity in your supply chain can provide a safety net.
Large International Retailers
Large international retailers usually have the resources and structures in place to manage the complexities of offshoring. However, the higher carbon footprint and potential sustainability issues should be taken into account in your decision making.
What Are the Best Countries for Sustainable Clothing Manufacturing – Where to Find Them?
A report published by the Geneva Center for Human Rights has determined that a product’s location is the biggest driver for fashion emissions rather than fibre type. It is because the sustainability impact of clothing manufacturing may largely depend on the energy mix of the country in which the manufacturing occurs. Countries relying heavily on renewable or low-carbon energy sources (such as wind, solar, or nuclear power) could potentially have a lower environmental impact compared to countries where coal or other high-emission energy sources dominate. This could significantly overshadow the environmental impact of the materials used in the clothing items themselves.
Therefore, evaluating the sustainability of a piece of clothing might not only involve looking at the type of materials used or the ethical sourcing practices, but also considering where the item was manufactured. This reinforces the complexity of achieving true sustainability in the fashion industry and underscores the need for a comprehensive approach that encompasses all stages of the supply chain.
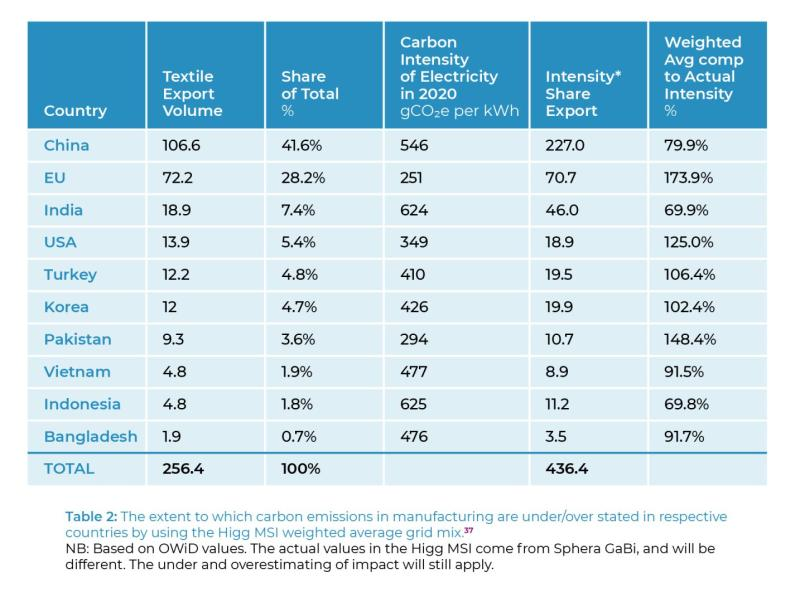
Emissions is just one factory that goes into the umbrella term sustainability therefore it’s worth exploring other impact factors such as social compliance.
The countries most frequently recognized as the best countries to source sustainable clothing include: Portugal, Sweden, Germany, Denmark, India, Turkey, and the US. It’s important to recognize that the term “sustainable” is multifaceted, and each nation comes with its own strengths and weaknesses. While no single country stands out as the supreme, understanding the respective advantages and disadvantages can aid in making informed decisions and taking steps for improvement. Below are summaries of each of these countries, how they operate and factors to consider if you choose to source from the country:
- Portugal
- Why Selected: Portugal has a strong textile industry with a growing focus on sustainable practices.
- Sustainability Reputation: Portuguese manufacturers often emphasize water and energy efficiency, and some factories specialize in recycling and organic materials. Portugal has strong labour laws ensuring fair worker treatment.
- Advantages: Portugal offers high-quality manufacturing, EU access, and shorter lead times for European-based brands.
- Negatives: Portugal may have higher manufacturing costs than some other countries, and language barriers could exist for non-Portuguese-speaking brands.
- Suitable for: Startups to large international retailers looking for high-quality, sustainable manufacturing within Europe.
- Sweden
- Why Selected: Sweden is a global leader in sustainability with a significant presence in the textile industry, including famous brands like H&M and Acne Studios.
- Sustainability Reputation: Sweden has a robust approach to environmental management and worker’s rights. Some manufacturers are leading the way in recycling, organic materials, and energy-efficient practices.
- Advantages: Swedish manufacturers offer high-quality production, innovative materials, and sustainable practices. The country’s strong labour laws ensure fair worker treatment.
- Negatives: Higher manufacturing costs are likely due to the high cost of living and stringent regulations. Language barriers could exist, but English is widely spoken.
- Suitable for: Ideal for startups to large international brands seeking top-quality, sustainable manufacturing within Europe.
- Germany
- Why Selected: Germany has a robust textile and fashion industry with a strong focus on sustainability, efficiency, and innovation.
- Sustainability Reputation: German manufacturers are known for their high standards in quality control, environmental protection, and labour rights. Many factories specialize in eco-friendly materials and energy-saving production methods.
- Advantages: German manufacturing provides high-quality, technologically advanced, and sustainable textiles. Germany is also centrally located for distribution within the EU.
- Negatives: Manufacturing costs in Germany can be higher compared to other countries due to the high standards and cost of living. However, English is commonly spoken, easing potential language barriers.
- Suitable for: Startups to large international retailers seeking advanced, high-quality, and sustainable manufacturing within Europe.
- Denmark
- Why Selected: Denmark, home to global fashion brands like Ganni and Samsøe Samsøe, is recognized for its sustainable outlook and innovative textile industry.
- Sustainability Reputation: Danish manufacturers prioritize green technologies, waste management, and organic materials. Denmark’s labor laws ensure ethical treatment of workers.
- Advantages: Denmark offers high-quality production, innovative sustainable solutions, and access to the EU market. Danish manufacturers are often willing to accommodate smaller order sizes, which can be beneficial for startups.
- Negatives: Like other Nordic countries, the cost of manufacturing in Denmark can be higher due to the high cost of living and strict regulations.
- Suitable for: Startups and mid-sized brands looking for high-quality, sustainable manufacturing within Europe, with a willingness to accommodate smaller production runs.
- India
- Why Selected: India has a long history of textile production, with an increasing focus on sustainable and organic fabrics.
- Sustainability Reputation: India is a major producer of organic cotton and other sustainable textiles. There are certified factories following sustainable practices, although it varies widely across the country.
- Advantages: India provides lower-cost manufacturing and a wide range of textiles, including artisanal techniques.
- Negatives: Consistency and quality can vary between manufacturers. Some factories may not follow sustainable or fair labor practices, so careful vetting is essential.
- Suitable for: Startups, e-commerce brands, and mid-sized retailers looking for diverse textiles and lower-cost manufacturing.
- Turkey
- Why Selected: Turkey is one of the largest textile and garment manufacturers in the world and is recognized for its quality and speed. Its textile industry has been growing in the sustainable sector with many manufacturers investing in sustainable and organic materials, energy-efficient practices, and waste reduction.
- Sustainability Reputation: Turkey has a variety of manufacturers, some of which have started to implement sustainable practices, and there are also factories specializing in organic cotton and recycled materials. However, the degree of sustainability can vary significantly among manufacturers. Additionally, Turkey is a significant producer of organic cotton, which aligns with sustainable fashion.
- Advantages: Turkey’s proximity to European markets allows for shorter lead times and lower transport emissions compared to Far East sourcing. The country offers a wide variety of textiles and clothing, high production capacity, and rapid turnaround times. Turkey is known for high-quality production, especially in denim and luxury segments.
- Negatives: While Turkey has labour laws to protect workers, enforcement can be inconsistent, so it’s vital to ensure your factories adhere to ethical labour practices. Political instability could potentially disrupt supply chains. Additionally, sustainability standards can vary widely between different manufacturers, which requires due diligence in selecting factories.
- Suitable for: Suitable for startups, e-commerce brands, and mid-sized to large retailers looking for a balance between cost, speed, quality, and sustainability. Particularly beneficial for those focusing on denim or looking for quicker turnaround times for the European market.
- United States
- Why Selected: The US has a diverse manufacturing industry with a growing focus on sustainability.
- Sustainability Reputation: There’s a broad range of manufacturers in the US, some of which have strong commitments to sustainable practices, including energy efficiency, waste management, and organic materials.
- Advantages: Manufacturing in the US can offer lower transport emissions for US-based brands, flexible order sizes, and quick turnaround times. It also avoids tariffs for the US market.
- Negatives: US manufacturing can be more expensive compared to countries with lower labour costs. The sustainability practices may also vary significantly between manufacturers.
- Suitable for: Startups, e-commerce brands, and mid-sized to large retailers looking for flexibility, quicker lead times, and a ‘Made in USA’ label.
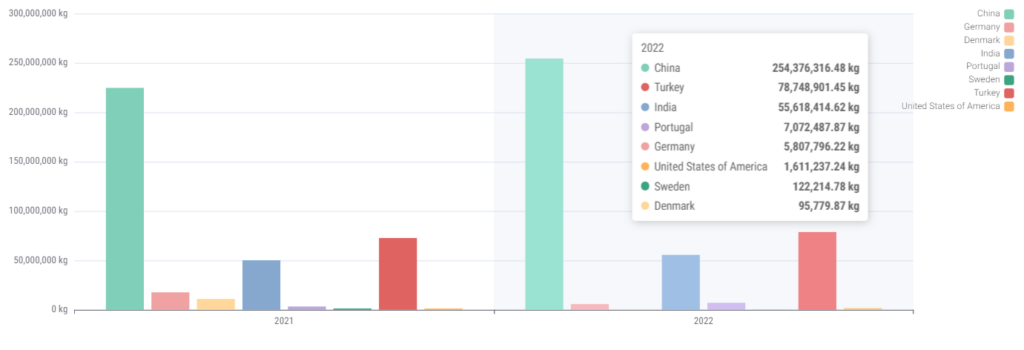
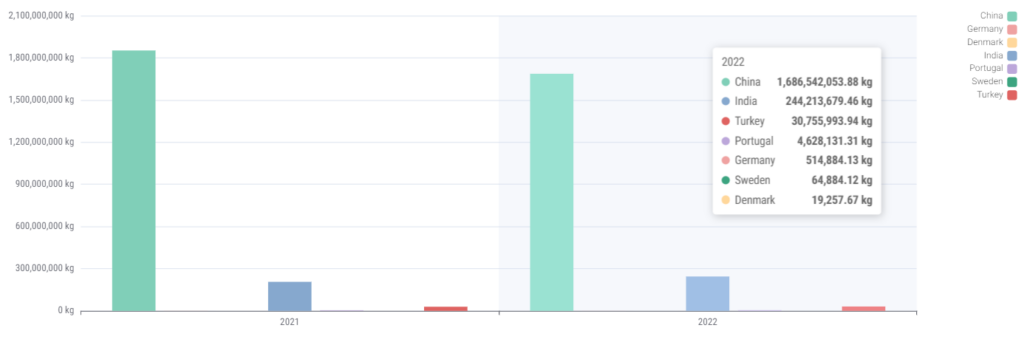
Below charts show the annual clothing import volumes from the countries highlighted above into the US and UK for the last two years. China has been included to demonstrate scale.
UK Clothing Import from Sustainable Listed Countries
US Clothing Import from Sustainable Listed Countries
Ultimately whether a factory is sustainable will largely depend on their setup, the technology and machinery they use and how they operate treat their workforce. This is where certification and compliance comes into play and the role it has within clothing manufacturing. Read here to find out more.
But how do you connect with these manufacturers? Here’s where Sourcing Playground comes into play. Our platform hosts a comprehensive database of factories globally that specialise in clothing manufacturing and hold sustainability certifications. Whether you’re a small start-up or a large retailer, you can find a perfect match for your requirements on Sourcing Playground.
Why not give it a try? Request a demo and get free trial access explore the possibilities of sustainable fashion manufacturing.